The market conditions that businesses face are in a constant state of flux which forces business managers to come up with new projects to compete and keep businesses relevant to modern consumers. Strategic planning describes the process a business uses to determine how it can best meet its objectives and carry out its mission. A SWOT-analysis is a common strategic planning tool that can help managers evaluate the chances that a certain project will succeed. It's also a common section found in strategic plan documents of public and private enterprises.
Defined as: "An analysis of the internal and external environmental factors performed as part of developing the organizational strategy"
The Basics
The term "SWOT" is an acronym for the words "strengths", "weaknesses", "threats" and "opportunities". A S.W.O.T framework involves composing lists of the internal strengths and weaknesses a business that is relevant to a certain project and then creating lists of opportunities and threats that exist outside of the company that could impact the project. For example, consider a tech company wants to increase its sales by expanding its product offerings. If the company owns a patent on a new type of computer processor technology, the patent could be listed as a strength, but if it the company does not have the resources to engineer and produce a prototype of the new processor, managers might list lack of capital as a weakness. Venture capitalists often invest in businesses with new ideas that have the potential for large growth, so the potential to attract venture capital could be listed as on opportunity. If competitors are in the process of developing similar technologies it could constitute a threat. Once all four lists are composed, managers can brainstorm ways to maximize strengths, limit weaknesses, take advantage of opportunities and avoid or reduce threats.
Video: Creating strategic plans and SWOT analysis with Strategy Designer™
How to Organize It
SWOT Analyses are often arranged as a 2 by 2 matrices with the lists of strength and weaknesses in the first two boxes in the first row and the lists of opportunities and threats in the second row. By arranging the analysis this fashion, the lists are separated into internal factors that can affect a project on the first row and external factors on the second row. In addition, the first column consists of the positive factors (strengths and opportunities) and the second column consists of negative actors (weaknesses and threats.). This method provides a simple framework to keep lists organized and conceptualize how the lists are related.
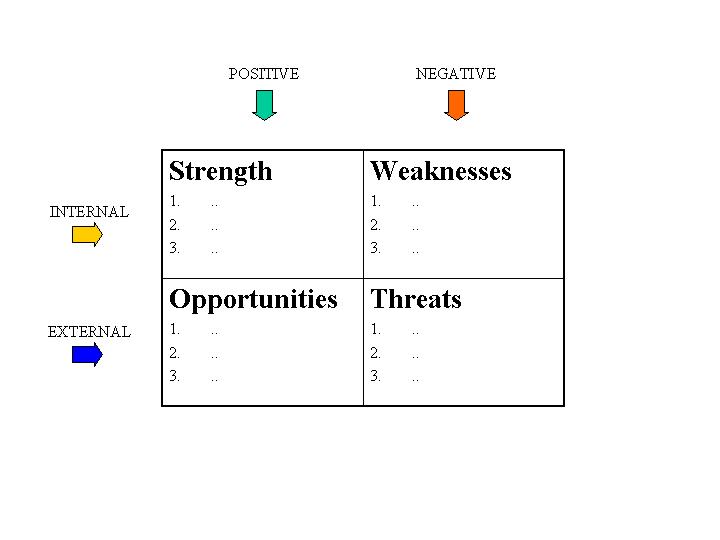
Purpose of a SWOT Analysis
The purpose of a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats framework is to get managers thinking about everything that could potentially impact the success of a new project. Failure to consider a key strength, weakness, threat or opportunity could lead to poor business decisions. For example, if the tech company with the patent for a new processor did not recognize the threat that its competitors were developing similar products, it might overestimate the sales potential of the new processor and take on debt to fund the development of the processor only to discover that the new product does not bring in enough revenue to pay off the debt. In other words, a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats brainwork can help managers avoid making costly mistakes and determine which projects are most likely to succeed.
About the author
Armin Laidre is a co-founder of ExitAdviser — an online DIY business-selling platform.
Read more from Wikipedia
